This repository has been archived on 2026-01-12 . You can view files and clone it. You cannot open issues or pull requests or push a commit.
b9abf6c7d31e7c54d4dbfbfab215cb03774bcba0
C language logging library logging
brief
Logging is a lightweight and easy-to-use C language log library that supports log level, log format, log output, log files, and other functions.
function
- Support log levels: DEBUG, INFO, Warning, ERROR, FATAL
- Support log formats: timestamp, log level, log content
- Support log output: console, file
- Support log files: automatic creation, automatic scrolling, log segmentation
install
- Conan
conan create .
- cmake
usage
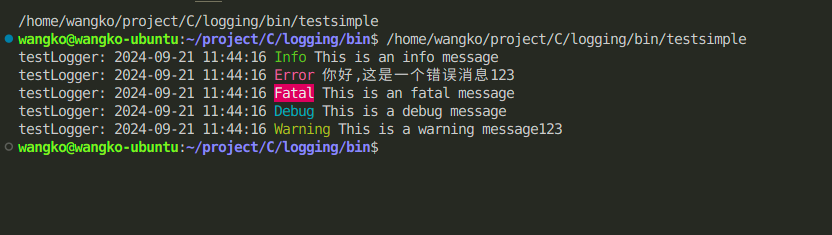
console log
#include "logging.h"
int main() {
Logger *logger = newDefaultLogger("testLogger", LOG_DEBUG);
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
destroyDefaultLogger();
return 0;
}
file log
#include "logging.h"
#include "logging/logging-handler.h"
int main() {
Logger *logger = newDefaultLogger("testLogger", LOG_DEBUG);
logger->addHandler(loggingFileHandler("test1", 1024*1024));
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
destroyDefaultLogger();
return 0;
}
Logging Interceptor
Support adding custom interceptors, currently with built-in substring interceptors The function of an interceptor is to redirect intercepted logs to the interceptor's dedicated processor
example
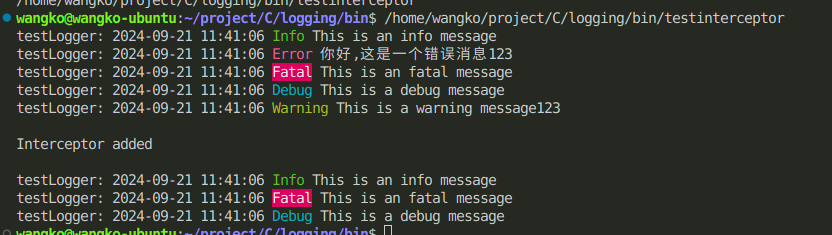
Redirects intercepted logs to a dedicated file processor
#include "logging.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
Logger *logger = newDefaultLogger("testLogger", LOG_DEBUG);
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
char *test1[] = {"123", "tt", NULL};
log_Interceptor *tint = loggingSubStringInterceptor(
test1,
LOG_DEBUG,
loggingFileHandler("test_interceptor", 1024 * 1024),
true);
logger->addInterceptor(tint);
printf("\n");
printf("Interceptor added\n");
printf("\n");
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
destroyDefaultLogger();
return 0;
}
Multiple substring interceptors
#include "logging.h"
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
Logger *logger = newDefaultLogger("testLogger", LOG_DEBUG);
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
char *test1[] = {"This",NULL};
log_Interceptor *tint = loggingSubStringInterceptor(
test1,
LOG_DEBUG,
loggingFileHandler("test_interceptor", 1024 * 1024),
false);
logger->addInterceptor(tint);
char *test2[] = {"123",NULL};
log_Interceptor *tint1 = loggingSubStringInterceptor(
test2,
LOG_DEBUG,
loggingFileHandler("test_interceptor1", 1024 * 1024),
true);
logger->addInterceptor(tint1);
printf("\n");
printf("Interceptor added\n");
printf("\n");
log_info("This is an info message");
log_error("This is an error message%s", "123");
log_fatal("This is an fatal message");
log_debug("This is a debug message");
log_warning("This is a warning message%s", "123");
destroyDefaultLogger();
return 0;
}